Step 2: How do LCD and LED LCD TVs work?
By Robert Wiley, Senior Editor
How does a LCD (Liquid Crystal Diode) TV operate?
The Basics: LCD TVs and so-called LED TVs work by blocking light. By sandwiching a solution of TN liquid crystals between two perpendicularly aligned panes of polarized glass, it becomes possible to manipulate the intensity of light as it passes through this crystalline matrix and out the glass panel at the other end. Depending on the voltage of the electrical charge running through them, liquid crystals will untwist so that the intensity of light able to pass through the second polarized pane is affected. Basically, these displays can switch between light states (where the liquid crystals are fully twisted) and dark states (where the liquid crystals are fully untwisted), or somewhere along the gray scale in between. The term "liquid" in liquid cyrstals is actually a misnomer as they are not a fluid substance but rather a hard crystal.
 Addressing: A liquid crystal display consists of an array of tiny segments-called "pixels"-that are manipulated to form images or to present information. Addressing is the process by which pixels are turned on (which disables the passage of light) and off (which enables the passage of light) so as to create an image on the polarized display pane in front of you. So-called active-matrix LCD TVs employ thin film transistors (TFTs), or tiny switching transistors and capacitors arranged in a matrix on a glass substrate, to direct electric charges down columns to reach a particular pixel. This, in turn, causes the liquid crystals to untwist and "display" a predetermined amount of light generated by the light source-usually a florescent bulb-in back of them.
Addressing: A liquid crystal display consists of an array of tiny segments-called "pixels"-that are manipulated to form images or to present information. Addressing is the process by which pixels are turned on (which disables the passage of light) and off (which enables the passage of light) so as to create an image on the polarized display pane in front of you. So-called active-matrix LCD TVs employ thin film transistors (TFTs), or tiny switching transistors and capacitors arranged in a matrix on a glass substrate, to direct electric charges down columns to reach a particular pixel. This, in turn, causes the liquid crystals to untwist and "display" a predetermined amount of light generated by the light source-usually a florescent bulb-in back of them.
Color (Re) Production: The light source in an active-matrix LCD TV is a series of florescent bulbs (called CFL or CCFL), or the more newly implemented LED (light emitting diode) backlighting (LED TVs) both of which emits white light through a polarized glass pane behind the liquid crystal solution. Theoretically, then, you can start with a white display: This is one where its liquid crystals are completely twisted and therefore able to direct the full spectrum of light out through the polarized display screen in front of you. Since all wavelengths can pass through, the full spectrum of light can be manipulated to create the desired color. To achieve a full color pallet on your LCD or LED LCD TV, each pixel is divided into three subpixels-red, green, and blue-that work in conjunction to determine the LCD pixel's overall hue. These subpixels are created by subtracting certain wavelengths, and the color(s) corresponding thereto, using special filters. By exploiting a combination of red, green, and blue subpixels of various intensities (or gray scales), a single pixel triad can reproduce approximately 16.8 million colors. Recently, Sharp Electronics has introduced the new Quattron Quad pixel technology which introduces a 4th color pixel - yellow. This increases the number of possible colors 4 fold.
8 steps to buying an LCD TV
- Step 1: What exactly is LCD TV?
- Step 2: How do LCD Televisions work?
- Step 3: What are the advantages of LCD Televisions?
- Step 4: What do you need to consider before you buy your LCD TV?
- Step 5: Installation Considerations
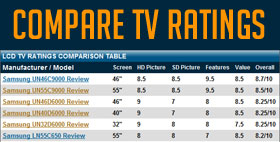
- Step 6: View the Top 10 LCD Televisions
- Step 7: How and Where to buy a LCD TV
- Step 8: Find reputable online LCD Televisions Dealers